With the rapid development of science and technology, MicroLED micro-display chips have become the key technical support for many cutting-edge fields. According to TrendForce's "2024 Near-Eye Display Market Trends and Technology Analysis" report, MicroLED is expected to occupy 18% of the AR device market in 2024. By 2030, the AR device market size is expected to reach 25.5 million units, and MicroLED's market share is expected to increase to 44%, showing a broad market prospect.
In addition, as the technology continues to mature, MicroLED's unique ultra-small size, ultra-high brightness and ultra-low power consumption characteristics will gradually replace the dominant position of DLP optical machines, and will further promote the upgrade of products such as micro projectors, digital car lights, 3D printers, and car HUDs.

In this technological competition, Hongshi Intelligent has successfully made a number of breakthroughs in the field of silicon-based MicroLED micro-display chips with continuous innovation and breakthroughs, becoming the focus of the industry. This article will share with you a series of exploration results of Hongshi Intelligent in the field of MicroLED technology in recent years.
Improved light efficiency: Breaking through industry bottlenecks
AR glasses have always been the "vanguard" in the field of MicroLED applications. It is reported that in 2024, 11 AR glasses manufacturers have adopted MicroLED optical machines as their imaging source.
However, due to the low coupling efficiency of diffraction optical waveguides, its eye brightness needs to reach 1000Nits, which means that MicroLED chips need to provide a brightness higher than 2.5 million Nits to meet the eye brightness index. The single pixel size of MicroLED chips is usually less than 10μm.
The improvement of the light efficiency of MicroLED micro-display chips involves the coordinated optimization of multiple technical dimensions.
1. The influence of size effect and the influence of peeling damage
In the past, traditional MicroLED manufacturing mostly used sapphire epitaxial wafer technology. However, sapphire substrate epitaxial wafers can generally only be made into 4 inches and 6 inches, while silicon-based epitaxial wafers can be made into 8 inches and 12 inches. For micro-display chip manufacturing, 8 inches and 12 inches have better performance and cost performance, but they are also quite technically challenging.
Sapphire substrate peeling is a lossy peeling, which will damage the chip epitaxial layer during the laser peeling manufacturing process, making it difficult to improve the essence of various light efficiency parameters. In sharp contrast, Hongshi Intelligent focuses on the MicroLED manufacturing process of silicon-based substrates. As a non-destructive peeling, the silicon substrate can avoid damage to the epitaxial layer, laying a good foundation for improving light efficiency.
Simply put, the size effect will significantly affect the epitaxial wafer EQE, and the change of the epitaxial wafer EQE will feedback and affect the overall performance of the chip.
At such a small scale of MicroLED, the behavior of microscopic particles such as electrons and photons will change. What is this concept? The diameter of a human hair is generally around 50-70μm. In contrast, the single pixel size of a MicroLED chip is much thinner than a hair.

Figure: Hongshi Intelligent Aurora A6 MicroLED micro-display chip
The correlation between epitaxial wafer EQE and size effect is determined by current density. In general, the test value of EQE by epitaxial wafer manufacturers is often based on a size of more than 40μ, and the EQE data for small sizes is basically missing. Obviously, this does not meet the applicable requirements of AR glasses products.
The Aurora A6 (single green) MicroLED product can achieve an EQE of more than 10% when the pixel pitch is 3.75μm; in the case of blue MicroLED, the EQE can reach 10% - 15%. This value further illustrates the excellent performance level of Hongshi Intelligent products in small-size applications.
2. Sidewall effect suppression
Similarly, as the size of MicroLED chips decreases, the proportion of sidewall area increases significantly. For example, when the chip size is reduced to 15μm, the sidewall emission ratio of MicroLED will increase by 184%, and the sidewall damage is often caused during the etching process of MicroLED.
The presence of more defects on the sidewalls of a single pixel of MicroLED will not only aggravate the quantum confined Stark effect (QCSE), but also make holes converge to the sidewalls, enhance non-radiative recombination (SRH), and make electrons and holes recombine in the form of heat energy instead of light emission, resulting in reduced light efficiency; at the same time, the inclined sidewalls will also increase the exposed area of the multi-quantum well layer, bring more defects, and enhance the charge coupling effect at the sidewalls, which is also unfavorable to the generation and emission of light, further reducing the light efficiency.
Simply put, from the perspective of crystal structure, the originally complete and regular crystal structure is destroyed. Just like neatly arranged building blocks are disrupted, the orderliness of the atomic arrangement of the crystal is broken, resulting in defects such as dangling bonds and lattice distortion.
In this regard, Hongshi Intelligent uses three methods to achieve sidewall repair.
ALD (atomic layer deposition) technology can accurately control the growth of thin films at the atomic scale. By depositing a specific material film on the sidewall through ALD, the atoms in the film can combine with the dangling bonds, thereby stabilizing the dangling bonds, reducing their capture of electrons and holes, and reducing non-radiative recombination.
A similar principle can also be achieved by coating, coating the sidewall with a suitable film layer, and the atoms of the film material react chemically or physically adsorb with the dangling bonds to neutralize the dangling bonds, reduce the activity of the dangling bonds, and reduce the impact on chip performance.
It can also be wet processed, using a specific chemical solution to contact the sidewall, and the ions in the solution react with the dangling bonds to convert the dangling bonds into stable chemical bonds or other stable substances, so as to achieve the purpose of neutralizing the dangling bonds, and ultimately improve the light efficiency and overall performance of the MicroLED chip.
3. Cavity structure optimization
The cavity structure design mainly improves the light efficiency of MicroLED and optimizes the light generation by optimizing the light generation, transmission and emission process. Reasonable cavity structure design can improve the electric field distribution inside the chip and promote more effective recombination of electrons and holes.
For example, by precisely controlling the size and shape of the cavity, the probability of electrons and holes meeting and recombination is greatly increased, thereby improving the efficiency of photon generation; secondly, it reduces the transmission loss of light, and effectively reduces the absorption and scattering of light during propagation by selecting high-reflectivity materials to make the cavity wall.
In general, Hongshi Intelligent effectively reduces the loss of light and improves the utilization efficiency of light in the cavity by optimizing the cavity structure design, allowing more light to have the opportunity to be emitted, thereby improving the light efficiency.
A well-designed cavity structure can significantly enhance the light emission efficiency. For example, the use of special structures such as microlens arrays can change the light emission angle, allowing light to be emitted more concentratedly from the front of the chip, reducing light loss on the sides and back. Data shows that the use of a cavity with a microlens array structure can increase the light emission efficiency by 40%. Optimizing the coupling interface between the cavity and the outside world can also reduce the reflection of light at the interface, further improving the light efficiency.
4. Selection of optical reflective layer
The impact of the optical reflective layer on the light efficiency of MicroLED is mainly reflected in the reflection, absorption and scattering of light. Its design and performance are directly related to the efficiency of MicroLED in converting electrical energy into effective light energy.
In the MicroLED chip, the light generated by the active area is emitted in all directions, and some of the light will be emitted to the substrate of the chip or other non-emitting directions. By setting an optical reflective layer at the bottom or side of the chip, the light can be reflected back to the front of the chip, increasing the amount of light emitted from the front, thereby improving the light extraction efficiency and improving the light efficiency.
On the contrary, if the material selection of the optical reflective layer is improper or the structural design is unreasonable, the light will be absorbed during the reflection process, causing light energy loss and reducing the light efficiency.
Hongshi Intelligence changes the propagation path of light by introducing a reasonably and effectively designed optical reflective layer. Reflect the light that might have been absorbed or escaped from the chip and could not be effectively used back to the active area or guide it to the emission direction. In a MicroLED with a specific structure, the optimized optical reflective layer can increase the light extraction efficiency by 30%-50%.
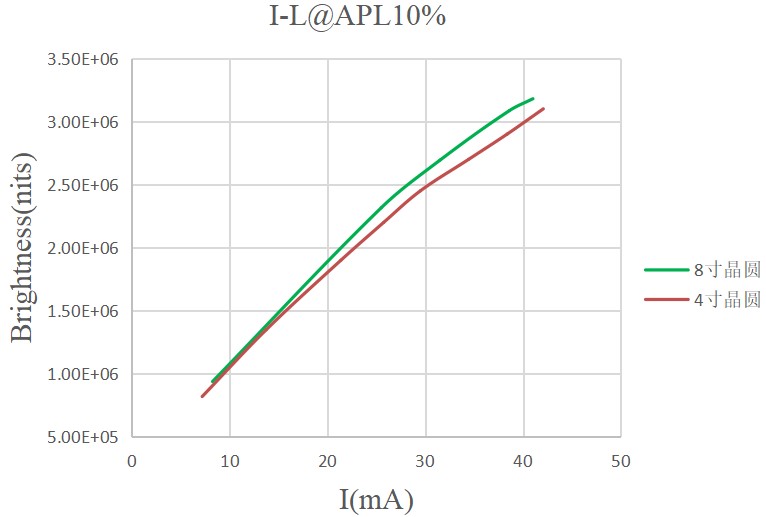
Figure: 4-inch and 8-inch wafer brightness curve with current
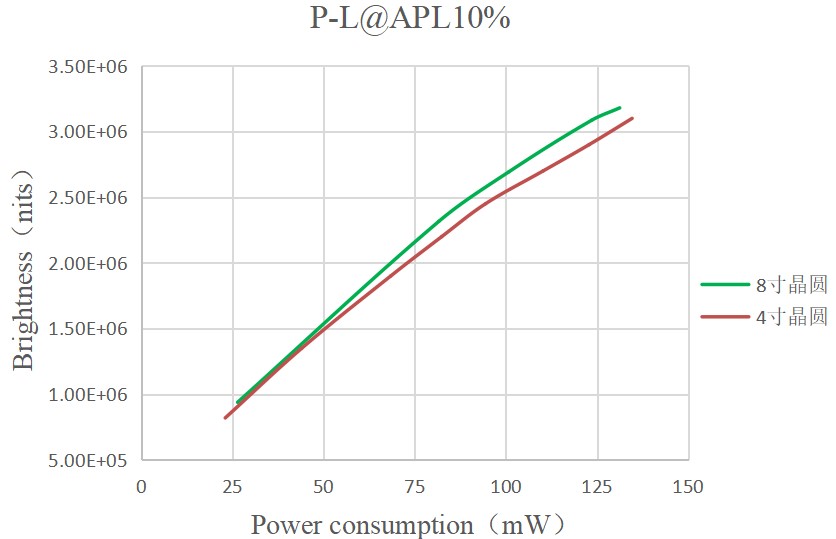
Figure: 4-inch and 8-inch wafer brightness curve with power consumption
It should be clear that even if the micro-MicroLED display chip can reach ultra-high brightness of millions or even tens of millions of nits.
But in fact, its pixels will not all emit light at the same time. Usually, the proportion of pixels that emit light at the same time is 10% - 15% or even lower. Therefore, the industry is accustomed to using APL 10% for measurement (taking a 640x480 MicroLED micro-display chip as an example, only 30,000 of the 300,000 light-emitting points are measured), which makes it easier for everyone to understand and unify the test method.
At present, the industry calculates the luminous efficacy value according to APL10%. At 0.12 single green, Hongshi Intelligent has successfully improved the average luminous efficacy of MicroLED micro display chips to 3 million nits (power consumption 100mW) after two years of technical research. This achievement marks that Hongshi Intelligent has achieved the highest level of mass production photoelectric efficiency in the global 8-inch silicon-based micro display chip field.